In the previous article we developed the topic of growth and development of an agile work ecosystem, the implications of collaboration, its scope and maturity to create a business transformation towards agile in a sustained way. We also review the importance of a framework, which aims to simplify a complex reality in order to identify critical needs, co-create meaningful solutions and deliver them in an iterative, incremental and emergent way, continuously learning and adjusting to the environment to better serve our customer.
Digital transformation is social energy in motion, a source of empowerment and ownership that resides in the interaction between all our collaborators, to better serve our clients.” MAMH (2020)
Today we will fly over 10 important points that are part of a transformation journey, using a growth metaphor, it is like a journey and each of these points represents the peaks that we must reach.
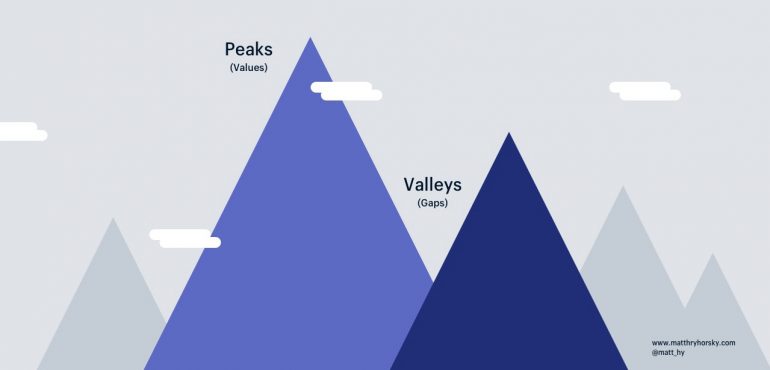
Figure 1: Business transformation implies growth of its capabilities.
Source: Miguel Martínez (2020). Own elaboration.
It is very important that when we want to build an agile business we do so through agile, which means growing and developing the work environment in a sustained way, defining the transformation cycles, releasing value in each cycle, carrying out an inspection and adaptation of the environment in each cycle, with the aim of increasing the organization’s capabilities according to progress, in such a way that in each cycle an organization with greater and different capabilities emerges that creates a positive impact on its collaborators and clients.
Hearing it told is not the same as the experience.” Chinese proverb
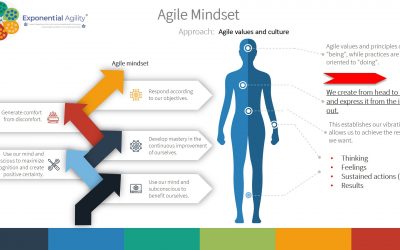
Figure 1: Business transformation based on a transformation of the person.

Source: Miguel Martínez (2020). Own elaboration.
Let us remember that organizations do not transform, those who do it are the people who belong to the organizations, they do it by transforming their internal dialogue, organizations are based on the exchange of meanings of those who integrate them.
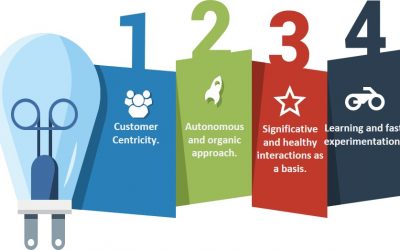
Figure 1: Areas and capabilities to build agility in the business.
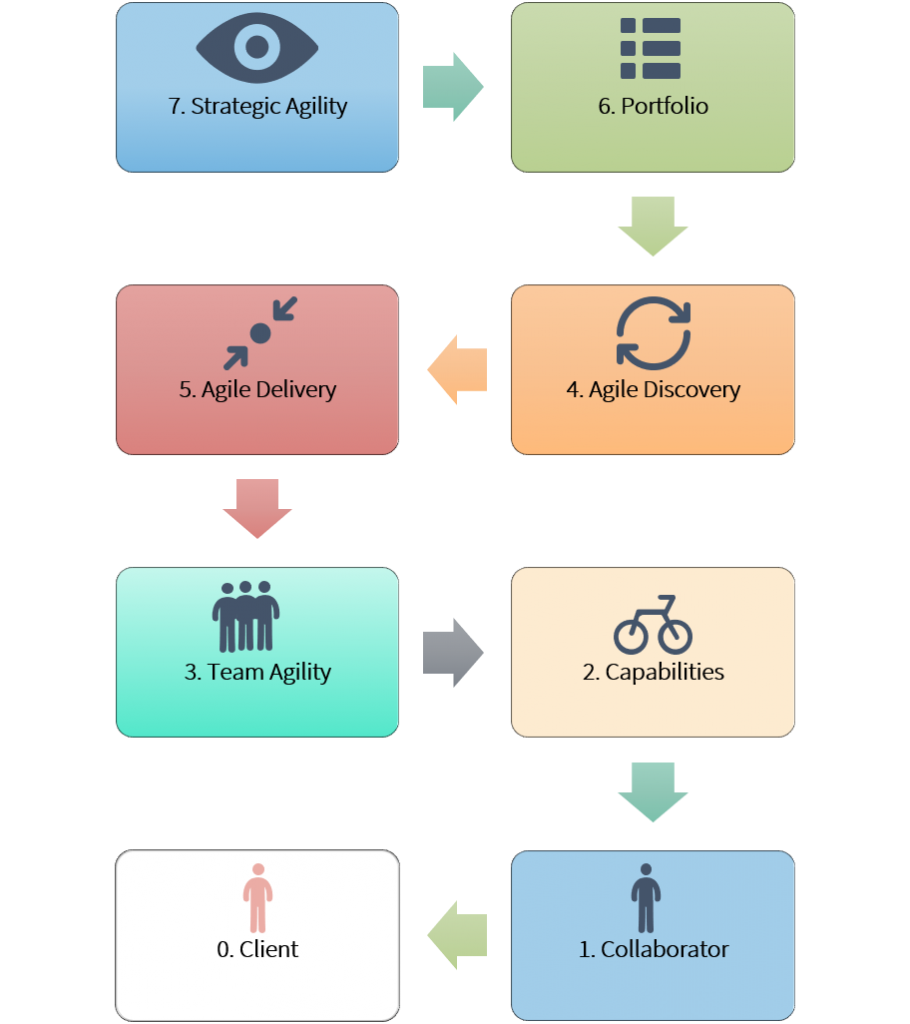
Source: Miguel Martínez (2020). Own elaboration.
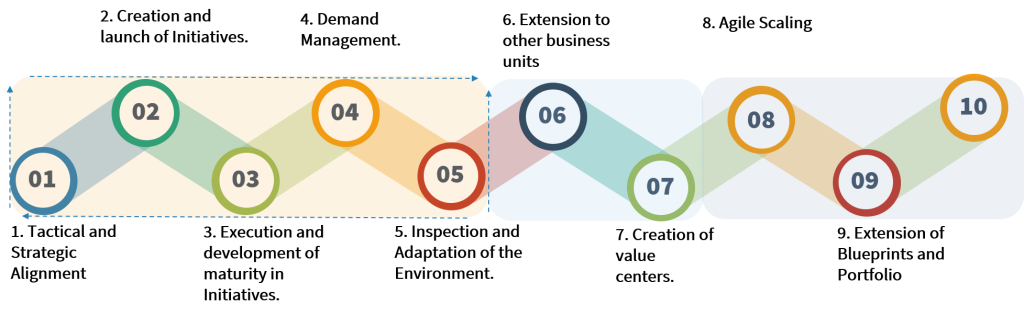
Next, we will describe the 10 capabilities that allow us to achieve an agile business MVP:
1.Tactical and strategic alignment.
Create a shared purpose and vision to inspire action, an alignment requires creating cohesion to the organization from the internal and external perspective, so that it is socialized through the co-creation of a strategy and a tactic of the transformation that we hope (future model). It is very important that leaders know in advance the value of agility and that we as catalysts accompany them in this process.
A baseline of the different target areas is very valuable, with respect to the current state of the business, with the purpose of obtaining and offering clarity of the impact of progress, in increasing capacities, let’s take an example: “At the fourth month once the transformation was implemented in a business unit, we achieved a positive impact: the decrease in operating costs, if we do not have a baseline, it will be very difficult to support the origin of this result with data ”. Let us remember that what we do, we must convert it into an installed business capacity, to create sustainability of a future operating model, being the principle of strategic agility in the scope of the transformation that is defined.
In this phase we also find, the prioritization of the initiatives that consists of defining the impact of the initiatives with respect to their type: savings, investment, profits, this definition is worked together with the transformation team, sponsors and representative of strategic level of the organization (“committed” steering committee). Once this prioritization is done, we have to understand the business model from the agile perspective for each of the selected initiatives, develop the preliminary product framework and outline the preliminary map of the creation of the product / service and those involved in the process.
2.Creation and launch of initiatives.
The objective of this increase is that for all the initiatives / teams created, it will be necessary for each team to focus all its participants towards the same objective, define and prioritize the initial scope of the product, obtain greater clarity about what you want to create, the priorities and risks involved. It is very important, in this phase, to manage expectations, the business vision, the joint understanding, the dependencies and stakeholders, the risks and their mitigation, as well as the construction map, the initial criteria of success and the quality of what visualize the participants, who are directly involved in the execution activities of the current projects, related to the business domain in question.
A person recently asked me, who decides who makes up an agile team? First of all, an agile team is made up of 3 to 9 people, in order to enable face-to-face communication, second, it must be a cross functional team, In other words, it integrates all the capabilities required to build the product in question, third, the team members should be people who are directly involved in the value creation process, not their bosses, not their managers, we look for teams that are self-organized and have the ability to respond themselves. We must respond to constant change and the context that exists in the current business, to progress. Obviously what touches here too, is to raise awareness of the product owners and those who at that moment are still the managers or directors of the functional areas, who open to become agile leaders, this is a process that takes on the same importance that the very creation of agile teams and that will be a topic of conversation later on.
Then, it will be relevant to confirm roles and provide basic training, in the frameworks to be used, once this is done for all the initiatives to be launched, we will formally proceed to confirm the assignments of these roles at the organizational level and we will launch the teams, consisting of the establishment of the start dates of the formal planning of the releases, of the cycles of delivery of results, the creation of the product log, the beginning of the planning and of all the events related to the framework selected (Scrum / Kanban / XP / Nexus / LeSS / SAFE).
Cultivating autonomy, based on the purpose, meaning and mastery in the tasks that each of the members performs is one of the central points in this stage. If you require support in this regard, you can contact us 😊.
Today we will advance here, if you have questions or comments about it, feel free to contact us directly and ask us.
Miguel A. G. Martínez H., september 2020,
Greetings to all,
Bibliography:
- AG, D. (2020, March 10). Respond and Recover | Crisis management in unprecedented times. Retrieved August 20, 2020, from https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en.html
- Allas, T., Sjatil, P. E., Stern, S., & Windhage, E. (2020, April). How European businesses can position themselves for recovery. Retrieved September 10, 2020, from https://www.mckinsey.com/
- Mitchell, C. (n.d.). The Conference Board – TCB C Suite Challenge 2020 Covid19 Recovery. Retrieved September 10, 2020, from https://conference-board.org/us/
- One, V. (n.d.). 14th Annual State of Agile Report. Retrieved September 10, 2020, from https://stateofagile.com/
- O’rreally, B. (2020, May 11). Scaling Innovation Means Descaling Work. Retrieved September 10, 2020, from https://barryoreilly.com/resources/
- Saenz, H., Supko, M., & O’Keefe, D. (n.d.). Why Return to “Normal” When You Can Recover to a Winning Position? Retrieved September 10, 2020, from https://www.bain.com/